Ultimate Classroom Design Checklist
100+ Things You Must Consider Before
Planning a Next Generation Learning Environment!
Share:
So many puzzle pieces work together when designing new learning spaces.
Architecture, people, and policies must align to create a pleasant and productive place to work and learn. We’ve compiled a list of 100 considerations for planning a new learning environment.
Many of these considerations are facilitated at the administrative level, but others can be implemented at the classroom level.

Section 1
Furniture
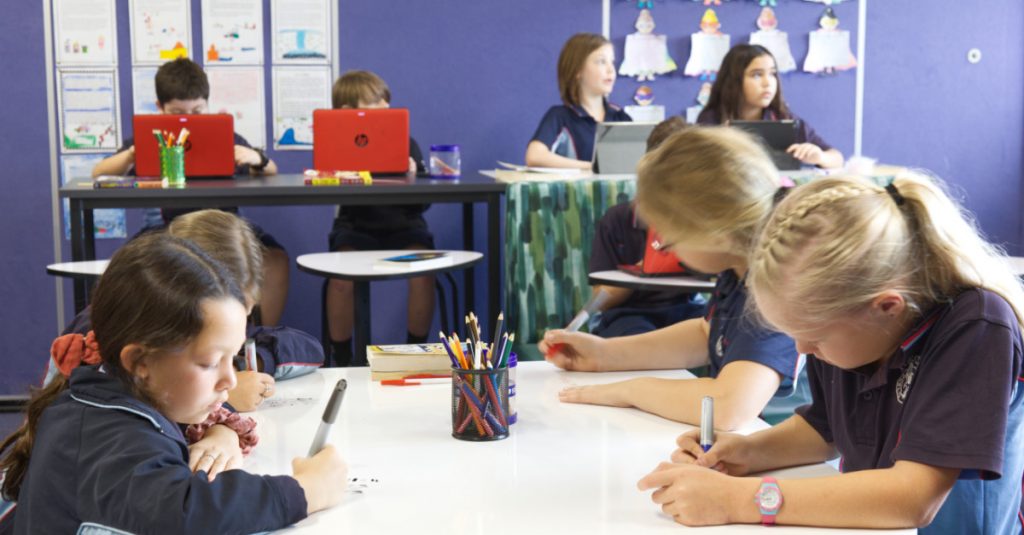
Choosing the right furniture for a next generation learning space is a very important decision.
Obtaining high quality, multi-purpose and agile furniture for students to use in learning environments will make a big impact on their learning outcomes.
The considerations below should be kept in mind when selecting furniture for classroom design and learning environments.
1. Agile
2. Seating
Both traditional seating and flexible seating options can be considered after weighing the pros and cons of both.
Wesley Imms, an associate professor at the University of Melbourne Graduate School of Education, warns in publication Education Week that although students are more creative and collaborative while using flexible seating, that teachers must change their instructional methods to encourage that creativity and collaboration as well.
3. Storage
With a rise in the number of students enrolled and the flexibility of classroom seating, it may be hard to fit in adequate storage solutions.
School News New Zealand points out that schools no longer have to worry just about storing books and backpacks. Electronic devices such as laptops and ipads also need to be securely stored away.
Storage solutions need to take into account flexibility and cost effectiveness.
4. Desking
Both the instructional methods and the class size may dictate which types of desks are appropriate for student learners. In a classroom space, you may need easily configurable furniture, large, round tables or more traditional student desks.
Teacher desks can also make a huge impact on the layout of the classroom.
When considering what type of teacher desk to include in your classroom design, think about both the space you have to work with and your instructional goals.
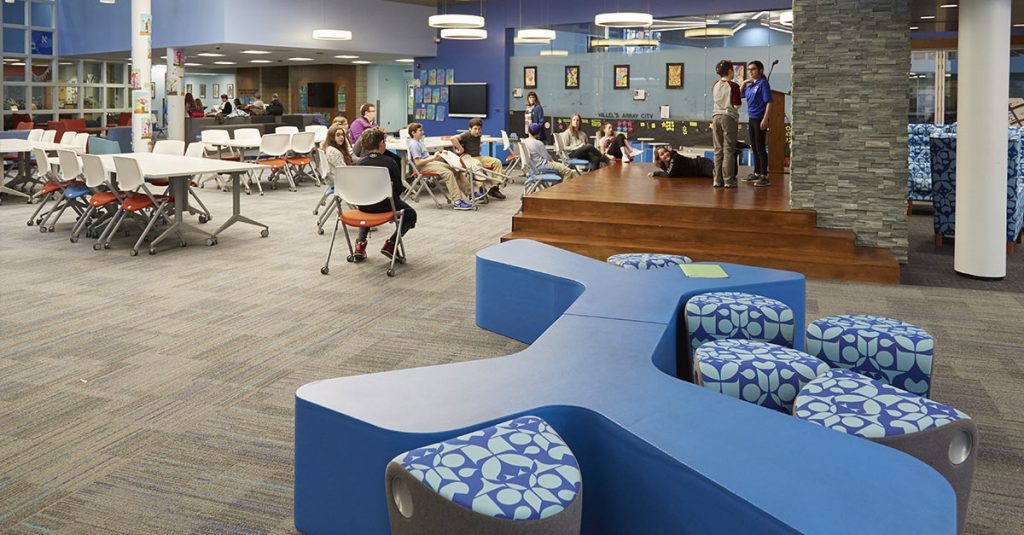
5. Zones
High school students may work in small groups on some days, listen to a lecture on others, and sometimes work independently.
Elementary school students frequently switch between zones or “stations” within a classroom. Light-weight furniture with wheels allows for a quick switch between zones.

6. Texture and fabric
Texture and fabric choices should account for functionality as well as aesthetics.
In a school setting, take into account how easily furniture can be stained or ripped and choose long-lasting fabrics.
7. Longevity
One must consider longevity when picking out furniture.
One problem with teachers putting together their own flexible seating options is that it often breaks and needs to be replaced, causing teachers to spend more money out of their pockets.
However, if comfortable yet high quality furniture is chosen to begin with, it is more likely to last one school year, and hopefully many years after that.
8. Colour
According to American School and University, children of different ages are stimulated by different colors.
Schools need to find colors that don’t overstimulate or under-stimulate their students.

9. Multipurpose
Multipurpose furniture can help maximise space in smaller classrooms and create storage solutions.
10. Country of origin
China tops the list of Top Furniture Exporting Countries, but with so many other countries on the list, it’s worth exploring the cost and quality of different countries of origin.
11. Furniture company
With many furniture companies out there, it may be hard to choose one. However, some companies specifically design school furniture and, like BFX Furniture, have a good reputation.
12. Height adjustability
Some office chairs, desk chairs, and even desks come with height adjustability features. These features can help teachers and students who can’t sit for long periods of time. For students with ADHD, standing can provide plenty of room for fidgeting.
13. Ergonomics
Ergonomics, simply put, is the study of how people and their workplace work together create the best working environment. When choosing furniture and workspaces, you should assess their ability to be modified for better ergonomics.
14. Comfort
Obviously, students will be sitting most of the day, so comfortable seating should be a priority.
15. Furniture mix (bar height, soft seating etc)
By including a mix of furniture types, teachers can ensure that students have flexible and comfortable options for any type of learning activity.
16. Strength and durability
For safety reasons, furniture strength and durability should be considered. Furniture that does not need to be replaced frequently also saves money.
17. Special needs items
Furniture for students with special needs can help them feel more comfortable in the classroom.
Students with Autism, for example, may prefer soft furniture or a space tucked away from the noise.
18. Timber
Wooden furniture tends to be more durable and is better for the environment.
Different types of timber create a different aesthetic and some last longer than others, so one should consider what type of wood is being used for their classroom furniture.
19. Writeable Surfaces
Writeable surfaces, such as desks with built-in white boards, allow students to sketch, doodle, and calculate at their own seats.
They can help reduce the amount of wall space required for large white boards.

20. Warranty
If a product breaks, you’ll want to know if it can be fixed and for how long.
Read the warranty on any furniture you chose to see under what circumstances it can be fixed or replaced.
Section 2:
Teachers
Teachers should be heavily involved with the classroom design.
Giving teachers an input enables them to create the best learning spaces for their students and empower their teaching style.
Teacher needs to be comfortable to be able to quickly and easily reconfigure the classroom to accommodate for their lesson plan.

21. Teaching style
Teaching style can dictate everything from the size of a classroom to the type of furniture. There are currently several distinct teaching styles, all of which fall under either teacher-centered or student-centered.
The University of South Carolina’s Center for Teaching Excellence has developed a list of pros and cons for both teacher-centered and student-centred approaches.
22. Teacher footprint
A teacher’s footprint in classroom design depends on factors such as where their desk is located and how much teacher-generated material hangs around the room.
Some schools are moving toward a more student-centered footprint by rearranging furniture and putting the focus on student work.
23. Teacher input
A 2018 Gallup poll of 500 teachers in America shows that teachers don’t feel that they have enough input in decision making at school.
When designing a new school, or making any significant changes to the learning environment, you should take teacher input into consideration whenever possible.
24. Team teaching
Team teaching is a method where two or more teachers collaborate to make decisions and deliver instruction for one class.
According to the BYU Center for Teaching and Learning, there are numerous benefits for both teachers and students.
Team teaching allows for an exchange of knowledge and ideas between teachers and builds relationships between them.

25. Latest pedagogies
Staff and teachers need to keep up in the latest pedagogies and incorporate them appropriately.
We know that not all students learn the same way, so it’s beneficial to choose methods that you think may be beneficial for your students.
26. Co Teaching
There are six different models for co teaching which you should consider when hiring staff and designing classroom structure.
These co teaching models allow for more individualised instruction and student engagement.
27. School Vision
A vision statement helps all stakeholders see a common goal.
Teachers and staff use a vision statement to help them achieve smaller goals, become stronger employees, and ultimately make their ideal working environment come to life.
28. School Values
Some schools decide on a code of ethics or values that their students and teachers must follow.
Character education programs, such as “Character Counts!” can also be incorporated into the school, which lists six pillars of character.
Value statements also inform the creation of classroom rules and expectations.
29. School Culture
Whether you’re planning a whole new school building, or just looking to rearrange your existing classroom, it’s important to consider the culture of your learning environment first.
How do you want your learning environment to be perceived by outsiders?
How do you want your students to feel in their learning spaces?
The culture of your environment will likely influence everything from what types of seating you choose to the books on your shelves, so spend some time thinking about it before you make any other decisions.
30. Multipurpose spaces
Sometimes, a teacher may have to share a classroom with another teacher. Some areas, such as the cafeteria, may be used as multi-purpose rooms, used as a gym, cafeteria, and/or classroom at different points of the day.
Principals and teachers need to take into account things like movable walls and storage spaces when designing multipurpose spaces.
31. Easy reconfiguration
When rooms are used for multiple activities, teachers must be able to easily configure the room to fit their needs.
Furniture choices and allowing for enough space can help with an easy reconfiguration.
32. Smooth transitions between zones
Teachers can be trained in, and practice, techniques that help students transition between zones, such as changing signals and call and response clues.
These transitions can help maintain order and help students stay on schedule.
33. Future focused learning
Future focused learning focuses on teaching students the skills they will need to thrive in a global society.
Methods of future focused pedagogy include engaging students in collaborative and reflective learning activities that allow them to use their skills to solve problems.
34. Learning Modes
Learning modes, or styles, are nothing new in education. The four main types of learning styles include visual, auditory, kinesthetic, and verbal.
Although there is some recent research to suggest that learning modes aren’t as significant as previously thought, teachers still use them as a guide to ensure that all students are engaged in the classroom.
Section 3:
Students
Students should be the centre focus of all classroom design.
All students have different learning styles and the learning space should be flexible enough to allow each one to feel comfortable and take ownership of their learning.
35. Learning styles and preferences
Students’ learning styles and preferences should be taken into account when designing learning activities.
Many teachers find that students become more engaged in classwork when they are asked to give their input on the activities.
If students are excited about their learning activities, they will engage in them more deeply and learn more in the process.
36. Student engagement
Student engagement encompasses all meaningful interactions that a student has while at school, including those with people as well as the learning process itself.
Teachers should take into account what kinds of learning activities will most engage their students.
For more information on student engagement, The National Association of Independent Schools in America has written a toolkit that specifically discusses the importance at the middle school and high school level.
37. Inclusivity
Inclusivity in education (often called inclusion) is the process of ensuring that all students have the opportunity to learn in a mainstream school, regardless of their disability, economic status, social emotional needs, race, ethnic group, etc.
Both the United States and Great Britain have inclusivity laws that need to be followed by schools at all levels.
38. Ownership
Student ownership is another way to ensure that students are engaged in the learning process.
According to soundout.org, student ownership develops when a teacher is willing to become a partner with the student instead of just a provider of information.
Students are also encouraged to pursue their own passions and make mistakes during their learning process.
39. Wellbeing
When teachers and administrators focus on student wellbeing, they are taking into account social and emotional states and how they affect student learning.
Schools need to consider whether school psychologists and/or a curriculum that addresses social and emotional needs should be implemented.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) in the United States, offers various resources for schools and parents to learn more about this important aspect of education.
40. Health
Likewise, schools need to address the various health needs of the student population. Staff needs to include qualified nurses and policies need to be made in regards to who can administer medication.
Healthy students are less likely to miss school and do poorly at school.
41. Change behaviour
Undesirable behaviours happen in any learning environment. Schools can learn about different ways to change behaviours, including taking into account environmental factors.
42. Belonging
Studies show that when students feel a sense of belonging at school, they are more likely to be enthusiastic at school and less likely to be absent.
Some recommendations for teachers include practicing active listening strategies, encouraging positive social interactions, and acting as a personal support system for their students.
43. Emotionally Connected
Feeling emotionally connected, also referred to as building rapport, is an important step between students and teachers.
44. Intellectually Stimulated
Students who are intellectually stimulated are more likely to participate and learn more.
That may mean a teacher has to come up with more challenging or hands-on activities.
Students should be given the opportunity to achieve more than just is required.
45. Successful Learning Outcomes
Learning outcomes are clear, measurable statements given by the teacher at the beginning of a lesson.
For students to succeed at those learning outcomes means they have mastered the skills through an assessment, whether that is a project, essay, or test.
Section 4:
Planning
When planning for good classroom design you want to carefully consider desired outcomes for your school.
Look at what other schools have done successfully for inspiration and plan how you will roll out the changes to create truly amazing next generation learning spaces.

46. Scope
Enrolment numbers can fluctuate, but it’s a good idea to consider your expected maximum enrolment and how many classrooms will be needed.
Small, manageable class sizes not only ensure that students receive more individualised instruction, they may make students feel more connected and encourage them to become more sociable.
47. Risk assessment
A risk assessment needs to be developed to identify potential hazards and who might be harmed by them.
Schools may need to include a number of points that other businesses do not, such as how to transport students with disabilities in the case of a fire, what to do when a child is injured on a field trip, etc.
48. Get inspiration
By visiting other schools, administrators can get inspiration for all areas of the school planning process, from designing the building to creating a unique curriculum.
49. Get expert advice
Educational experts might include college professors, educational technologists, principals, seasoned teachers, superintendents, developmental psychologists, etc.
All of these experts have a unique perspective on education and may be able to provide you with ideas you might not have thought about before.
50. Desired outcomes
What do you want students at your school to achieve, and how can working with the school or larger community help your students achieve those goals?
51. Roll out implementation (Pathfinder)
Rolling out a plan for implementing changes is an important step to creating a new learning environment.
You can test new spaces by creating pathfinder projects.
52. Budget
Budgeting for a new learning environment requires a multi-step process, work towards a realistic budget based on available funds.
53. Floor plans
Floor plans are drawn up before a school can be built or remodeled.
They allow for easy access to room measurements to ensure that the furniture can fit the intended spaces.
54. 3d renders for visualization
3d rendering with a software program can show your school from multiple angles, creating the most realistic visual representation of what the school will look like once it is completed.
55. Determine timeline
Creating a timeline of important steps will ensure that everyone involved will stay on track, with a deadline for opening the new school on everyone’s mind.
56. Measures for success
Success looks differently to everyone, so determining how you will measure success will help everyone work toward a common goal.
57. Spatial awareness
Young students may have a poor sense of spatial awareness, or understanding of how objects are located in relation to them, so be mindful of this when considering classroom design.
Section 5:
Social & Community
Involving the students and parents not only in the initial planning of classroom design but the ongoing discussion about the learning space can be very beneficial.
The more the school is connected to the local community, the more it can thrive.

58. Involve students in the design process
Students feel more connected to schools when they feel their input is valued.
A student representative committee could be formed when designing a brand new school or you can involved students in the classroom design process.
Teachers can also get student input on class rules and activities at the beginning of the school year, which creates a greater sense of community.
59. Provide ongoing discussion opportunities
Teacher and student input can’t just stop once a school is built.
By providing ongoing discussion activities, administrators can create a greater sense of community.
60. Prepare teachers for change
The world is constantly changing, and so are a teacher’s roles and responsibilities.
Among the things that teachers need to be prepared for are changes in curriculum and methods, the inclusion of new technologies, and the implementation of online learning when necessary.
61. Trial teaching approaches
Trial teaching approaches include discrete trial teaching, a method in which students are given a reward or consequence for responding to steps in a complicated task.
Discrete trial teaching has been shown to help students who lack social skills
62. Welcome parent and community input
Parents should be an important part of the school community, so teachers should be open to a reasonable amount of parent input.
According to The Afterschool Cooperation of New York City, studies show that students whose parents are involved at school get better grades.
It may be hard for some teachers to allow parents to become involved, but it helps build a greater sense of community within the school.

63. Supporting Local Businesses
By supporting local businesses, schools can create mutually beneficial long-term connections within the community.
Local businesses may be willing to donate prizes or gifts to already existing customers, or host students for internships, part time jobs, and volunteer opportunities.
64. Australian Made Products
By purchasing products made within the country, you are supporting the country’s economy and its workers.
Looking for a country of origin label will help you identify products that are locally made or locally sourced.
65. Social Interaction
Providing opportunities for students to create positive social interactions with their peers and teachers is one way to create a sense of community.
Cooperative learning can be achieved only when a sociable learning environment has already been created.
66. Academic Research and Findings
When creating a new school, administrators should do research into other academic programs and curriculums.
These findings can help inform the decisions they make.
Section 6:
Technology
67. Accessibility
Not all students have technology accessible at home. In the USA, an estimated 9 million children don’t have internet access at home.
To make up for these inequalities, many schools budget for purchasing laptops or wifi hotspots for students in need.
68. Virtual spaces
Virtual spaces, such as virtual reality platforms, are becoming a more popular tool in learning.
Marc Erich Latoschik, who developed ViLeArn as a way to study how virtual reality can enhance education, believes that it may be helpful as a learning tool in the future, as blended learning becomes more popular.
69. Power and data
Experts need to be hired to ensure that the building can handle the electricity and data output used by technology in the building.
70. Apps/software
There are so many educational apps and software to consider.
Among the most important right now are online learning platforms and course management systems. A school needs to take into account pricing and features for each platform before deciding which will work for them.
Check out our 20 Must Have Apps for the Classroom Post.

71. Online safety/security
Schools often create online safety and security policies for their students and/or block undesirable websites and content on school computers.
On cyber safety and the responsible use of digital technologies, the Department of Education (VIC) outlines measures schools must take to support students to engage with digital technology in a safe and responsible way.
72. Online learning
With an increasing number of schools currently providing online instruction, it makes sense to consider online learning options.
Perhaps your school will have classroom instruction three days a week and remote learning the other two.
Maybe you want to give your students more freedom as to when they participate in learning activities, so flexible learning schedules might make sense for your school.
73. At home learning
Who will support your students when they learn from home?
Will they have the technology needed to participate in online learning?
Schools must account for factors that could leave students behind and be willing to provide the necessary tools.
Section 7:
Environmental
74. Room size
Classroom design needs to take into account the room size.
The size of the room needs to be large enough for students and teachers to move about freely, while taking into account storage space as well.
Of course, room size correlates with the number of students in the class.
The National Education Association (NEA) in America, recently published a policy brief about class size, which outlines research studies going back as far as twenty years that show that a reduction in class size leads to educational gains across students of all races and income statuses.
75. Indoor air quality
Healthy air quality can greatly reduce the risk of illness and reduce absenteeism.
Students who are exposed to unhealthy air quality can experience coughs, headaches, and exasperation of already existing asthmatic symptoms.
The EPA in the United States, has published guidelines for improving air quality in schools.
76. Noise reduction / Acoustics
According to The American Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA), both background noise and reverberation can lead to students paying less attention, not hearing or understanding the teacher, and exhibiting poor behavior.
Teachers can place rugs throughout the room, angle the furniture, and put soft tips on the bottoms of furniture in order to reduce unnecessary noise and reverberation.
Special noise reduction products can be hung on the wall or propped on the floor to reduce reverberation.
77. Visual aesthetics
Recent research suggests that emotion and cognition rely on each other.
Therefore, if a school or classroom evokes positive emotions, students will be more successful.
Design choices such as layout and color scheme can make a learning environment either more or less appealing to students.
78. Artificial Lighting
If you’ve ever worked in a school building, you’ve likely had to sit under artificial lights.
Artificial lights have been linked to eye strain and headaches, plus traditional light bulbs burn out frequently and use up a lot of energy.
If you must use artificial light in a building, consider installing LED lighting, which uses less energy, and look into blue light filters that can lessen the strain on the eyes.
79. Natural Lighting
A movement called “daylighting” has recently begun influencing school model design. Daylighting uses skylights and windows to bring natural light into a building.
In the United States, the Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy outlines the financial benefits of using daylighting principles in building design.
However, studies also show that productivity may actually increase when people turn down artificial light and open window blinds to let in natural light.
80. Bring the outdoors
During long periods of time in which we are forced to work indoors, such as in the winter, we tend to feel less focused, sluggish, and get sick more often.
With a few easy steps, school designers and teachers can bring a bit of the outdoors inside.
The National Association of Independent Schools in the United States, outlines how bringing plants, sunlight, and fresh air into our learning environments can help our students stay motivated.
81. Colour and texture
The link between color and psychology is nothing new.
According to Psychology Today, green tends to make us feel more creative, whereas yellow is usually off putting.
What colors and textures you use in your school can have an impact on how staff and students feel about their environment.

82. Temperature
When done properly daylighting can help hold heat in during colder months and keep heat out in summer months.
However, most school designers also have to think about other heating and air conditioning factors. Providing sufficient air conditioning to an entire school can be expensive, but there is some evidence to suggest that extreme heat can affect student performance.
In a 2018 study by Harvard University, researchers showed that as the temperature increased in a classroom, the learning proportionately decreased. Therefore, they argue, the benefits of air conditioning outweigh the cost.
83. Ergonomics
Ergonomics reduces work hazards and increases productivity.
Awkward work postures can create injuries, so ensuring that work spaces are designed well and that staff are trained in proper techniques for lifting and reaching can reduce injuries.
Section 8:
Cultural

84. Reflect culture perspectives
Schools are made of diverse learners, so their school environment needs to be one that reflects their cultural perspectives.
In addition to any school-wide initiatives, teachers can foster cultural awareness in their classrooms with some easy steps.
85. Mobility needs
Students can have limited mobility due to a number of illnesses and injuries.
Kidshealth.org breaks down some of the accommodations schools need to be prepared for, as well as some things that teachers need to consider teaching strategies and classroom design.
86. Sensory needs
Many students with ADHD or on the Autism spectrum have sensory needs. The students may be sensitive to lights, noise, screens, touch, etc.
In addition to classroom adaptations such as quiet spaces, teachers can supply fidget toys, weighted blankets, and fine motor activities, says The American Montessori Society.
87. Special needs
“Special needs” is a term that encompasses so many things, including medical, emotional, and learning problems.
In the United States, The Individuals with Disabilities Act (IDEA) provides a free public education to children with disabilities and gives parents a voice in their children’s education.
Schools also need to hire and train qualified teachers and support staff to help students with special needs.
88. Religious/spiritual needs
Accommodating the religious and spiritual needs of your students can be tricky.
How you approach these needs may depend on what country you’re located in and what type of school you are.
Administrators should be aware of the policies set up in their area.
Section 9:
Pedagogy
Taking into account the types of pedagogy that are going to be used in the learning space is an important consideration.
From Gamification to Play Based Learning, there is a huge range of pedagogies available to teachers.
89. Flipped learning
One pedagogical approach to consider, flipped learning, allows for students to study and explore on their own, with the teacher acting as a facilitator of learning.
The Flipped Learning Network is a good starting place for teachers who are curious about this approach.
90. Curriculum in new ways
By embracing creativity and innovation, teachers can take a curriculum and teach it in new, exciting ways.
In addition, there are many different types of pedagogy that teachers can experiment with.
91. Gamification
Gamification is a pedagogy that includes incorporating gaming elements into learning activities.
By offering experience points (XP) or “leveling up” milestones, teachers can motivate students to reach benchmarks.
Benefits of gamification include a more fun learning environment and students taking ownership over their learning.
Check out Article on Gamification in the Classroom!
92. Play based learning
The National Association for the Education of Young Children (NAEYC) stresses the importance of play in early childhood education.
They cite many studies that show that play helps children’s development in key areas, including language and social and emotional development.
Play based learning can also be incorporated into elementary school classrooms as well.
93. As a Catalyst for change
Teachers have a responsibility to inspire students to work towards changing inequalities in the world.
To the end, pedagogy can be used as a catalyst for that change.
94. Any other relevant pedagogies to consider
With so many different pedagogies out there, educators should familiarise themselves with any others that seem relevant to their grade level and subject matter.
Section 10:
Safety
In planning classroom activities, a risk management approach needs to be taken.
Teachers need to identify potential hazards, assess risks and select the most appropriate way of eliminating or controlling them before undertaking activities with students.
Departmental policies and procedures must be considered when planning classroom activities.

95. Non slip flooring
Slips and falls in schools are common but dangerous. At least some slips and falls can be avoided while designing the flooring surface.
Wax surfaces should be avoided. Instead, non slip alternatives such as carpeting and rubber can be installed.
96. Adequate space to move
Providing students with adequate space to move around can prevent safety issues and accidental injury.
97. Rounded corners
Furniture with rounded corners is safer for younger children, who may bump against them and get hurt.
98. Evacuation plan
Schools should have evacuation plans in case of a fire, natural disaster, or intruder. FEMA in the United States, has published an example evacuation plan that schools can use to model their own.
99. First aid
In addition to keeping a first aid kit on site and hiring a school nurse, administrators can look into the feasibility of training staff in first aid and CPR in case emergencies arise.
100. Safe furniture
Strong and durable furniture not only lasts longer, it’s also safer. Students are less likely to break well-made furniture, resulting in fewer injuries.
101. Furniture tipping
We’ve all heard horror stories of dressers or bookshelves falling over on children.
That’s why our furniture should have wide legs or solid bases and be anchored to walls whenever possible.
102. E0
Government requirements for schools is to have all boards with low formaldehyde emissions (E0).
Formaldehyde is a colorless, harmful gas that can cause cancer in the nose, mouth, throat, skin and digestive tract.
E0 is the amount of formaldehyde released less than or equal to 0.5 mg/l.
103. Maintenance
It’s important to have a regular maintenance staff responsible for upkeep of the building, grounds, and furniture in order to maintain a safe learning environment.
104. Furniture Stewardship/lifecycle management
Many furniture companies have committed to using recycled products and refurbishing existing products.
Choosing these products means you will be making less of an impact on the environment.

We deliver anywhere in Australia, New Zealand & South East Asia. Contact Us today for a FREE on-site consultation.