What is Future Focused Learning?
Although, the Future Focused Learning philosophy and variations of the ‘6 Cs’ theoretical framework has been a prominent pedagogical approach for the better part of a decade…
Our iteration is adapted from Michael Fullan’s 2014 New Pedagogies for Deep Learning and offers new insight in how modern and flexible learning spaces can make a difference to student learning.
In recent years, Future Focused Learning (FFL) is becoming a universally acknowledged approach in Australian and New Zealand schools.
In fact, the term ‘Future Focused Learning’ and ‘Future Focused Learning Environments’ is also now recognised by the NSW Department of Education.
However, our version of the Future Focused Learning philosophy is grounded in evidence-based space design and research from a variety of initiatives from the Australian Research Council like the Innovative Learning Environments & Teacher Change project (ILETC) and the Learning Environments Applied Research Network (LEaRn) at the University of Melbourne.
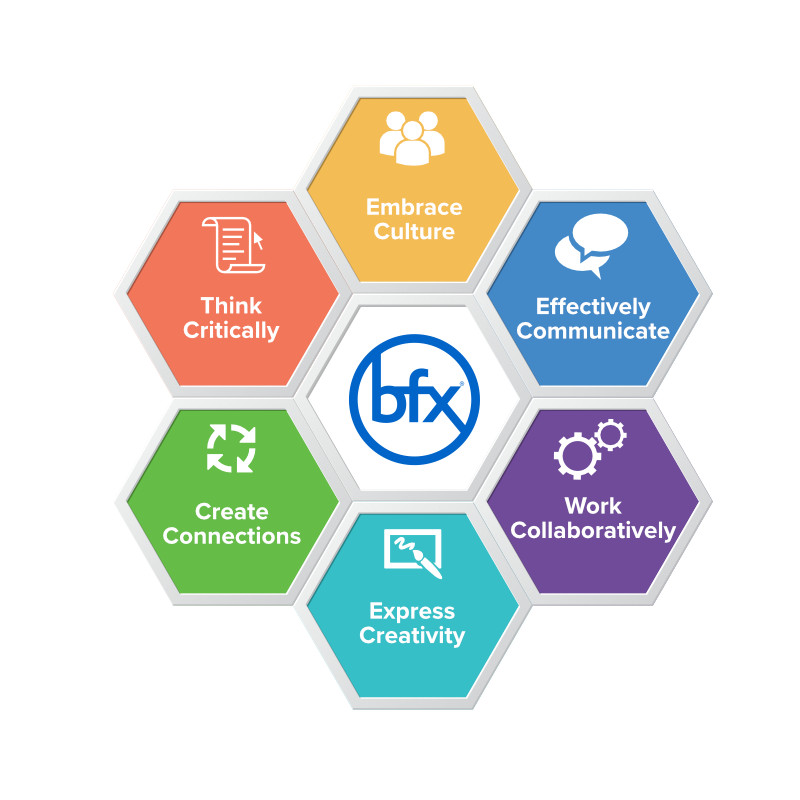
The aim of the FFL and ‘6 C’s’ framework is to assist students in developing their ‘future-focused skills’ or you may have also heard the phrase ’21st-century skills’.
Both terminologies essentially refer to the same idea.
In order for students to be able to succeed in our fast paced technology-driven world they need to be able to:
Think Critically
Effectively Communicate
Create Connections
Express Creativity
Work Collaboratively
Embrace Culture
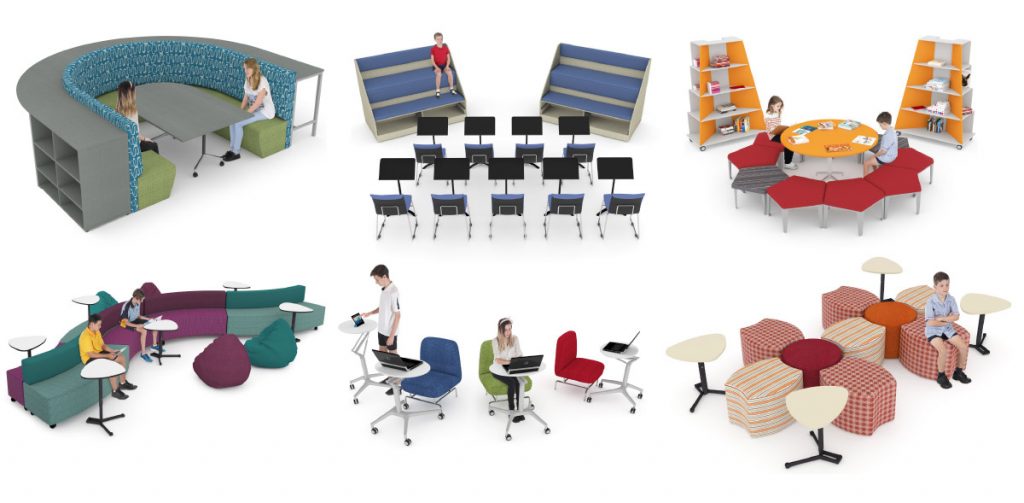
Discover Our Future Focused Learning Zones
The Future Focused Learning Zones
Future Focused Learning Zones are exactly that. They are focused spaces that facilitate different types of learning in the classroom. The physical classroom environment is more than just a ‘backdrop’ in the education industry.
In fact, it’s been often referred to now as the ‘Third Teacher’. Research confirms that the learning environment has a huge impact on student engagement. From lighting, temperature, acoustics and even furniture arrangement.
Our Future Focused Learning Zones are flexible, mobile and easily adaptable to suit student’s different learning styles or the needs of the learning activity.
How Do Future Focused Learning Zones Work?
- They are flexible and easily reconfigurable.
- They support different modes of learning including small group, large group and individual learning.
- They allow students to choose how and where they learn best.
- They can help facilitate more than one of the ‘6 Cs’ at a time.
- They incorporate active seating and height adjustable solutions to encourage more activity, engage core strength as well as promote better concentration and balance.
- They help reflect a bright and positive classroom culture.
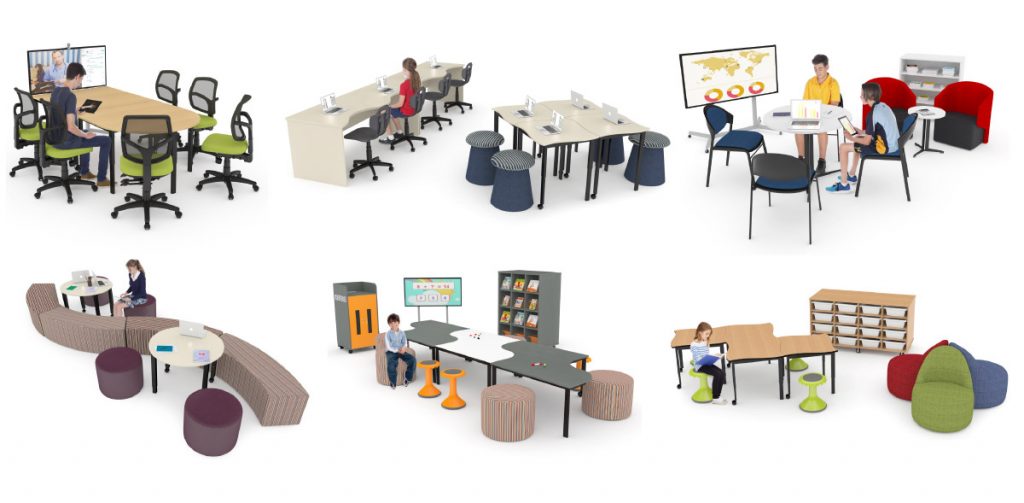
Connect Zones
Connectivity in the classroom allows students to get in touch with each other, the community and the real world. The key to unlocking student’s academic potential is opening them up to the idea of asking questions.
Furniture that allows for seamless technology integration in the classroom is essential here.
Whether it be with iPads, tablets or smartboards. Incorporating interactive whiteboards and easily movable soft seating into the space will motivate students to engage with one another as well as the content.
Benefits:
Students can then connect to each other and learning resources in order to find the answers. Connect Zones provide a safe and supportive space in which students can build positive and meaningful relationships with their peers, teachers and with their learning.
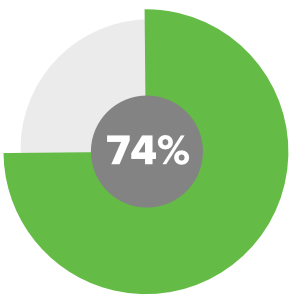
74% of educators surveyed said technology is key to helping them expand classroom content.
“Building relationships with students is about meeting students where they are, attempting to understand them, and developing connections with them.”
H. Richard Milner IV, Associate Professor
Connect Zone Examples

Collaborate Zones
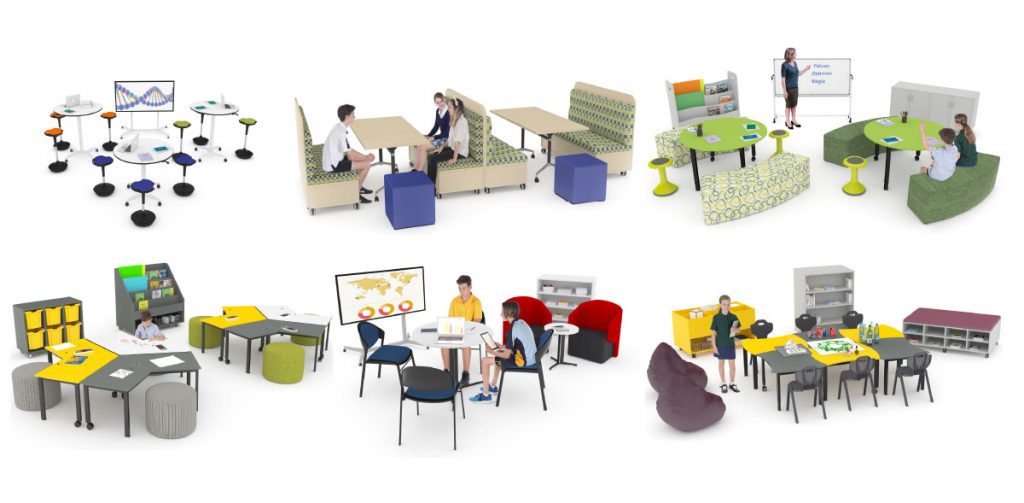
Collaboration in the classroom emerges when students are free to work together in small or large groups.
Collaborate Zones are flexible and supportive spaces in which students can arrange and rearrange settings according to how they best work together.
Collaborative learning ultimately promotes the exchange of ideas between students and leads to higher levels of productivity, teamwork, increased information retention and increased confidence. It also assists in strengthening their social skills.
Benefits:
Typically, people spend 65% of the work day collaborating and communicating with others.
A study recording student outcomes in mathematics when using group work to solve problems revealed;
70% of students found group work to be more helpful than individual work.
“Flexible classrooms give students a choice in what kind of learning space works best for them and helps them to work collaboratively...”
Edutopia
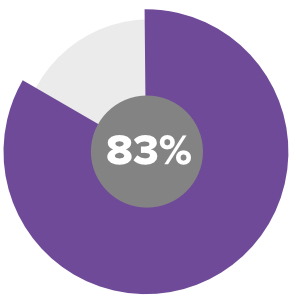
83% of students felt working in groups to learn math had a positive effect.
Collaborate Zone Examples

Communicate Zones
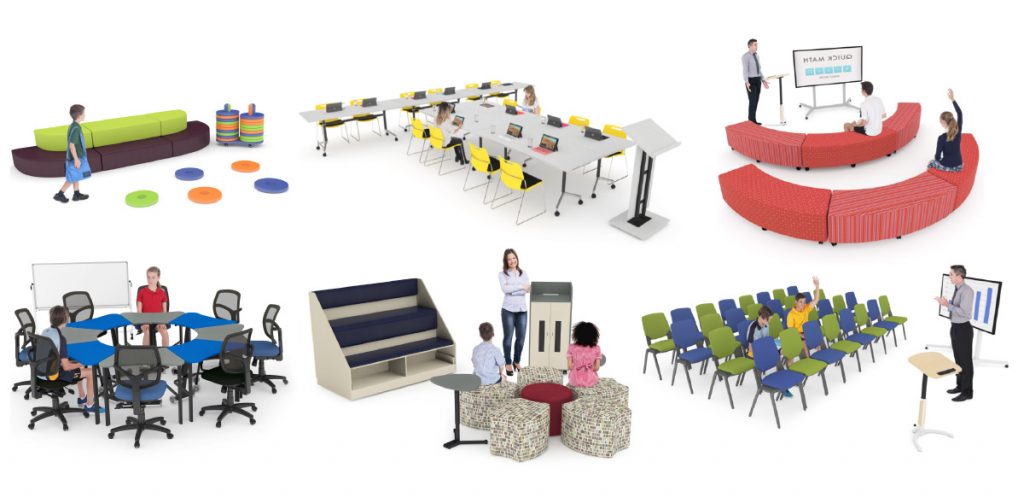
Communication can flow freely and most effectively in learning environments that incorporate a
combination of small intimate spaces and group spaces that encourage the sharing of ideas.
Communication Zones promote active discussion around conference-style configurations. They also provide the multi-purpose furnishings and resources that allow students to illustrate ideas, delegate tasks or brainstorm topics.
Benefits:
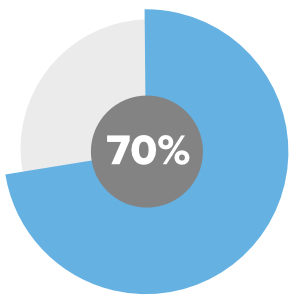
70.2% of employers consider communication skills as the most desirable attribute on a resume when hiring college graduates
"Communication is paramount in education. Whether it is teacher to teacher, student to student, teacher to parent or vice versa... communication is needed to make sure our students are successful"
David Andrade, Education Technology Specialist
Communicate Zone Examples

Critical Zones
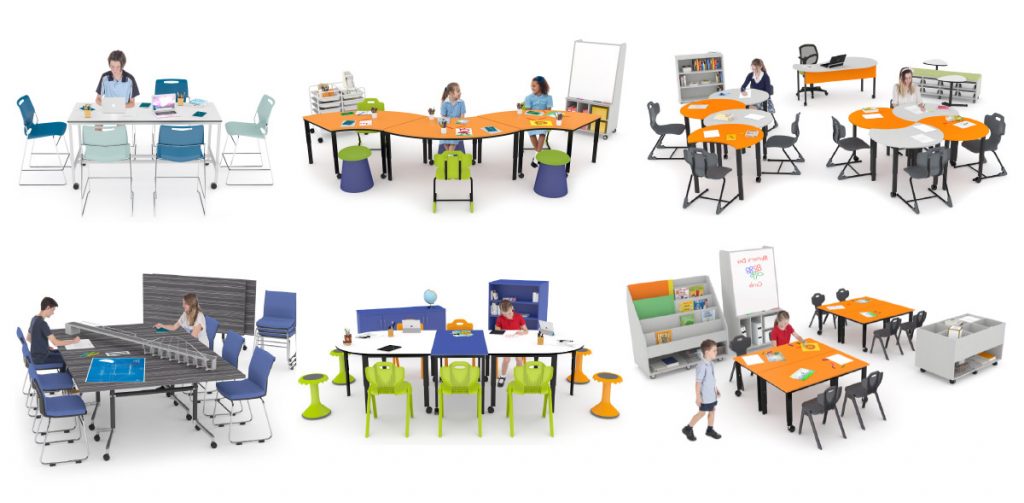
Critical thinking in the classroom involves students learning how to problem solve, analyse information and unpack ideas. It is through exercising critical thinking skills that students develop a more comprehensive understanding of a topic and learn how to apply their knowledge to real world scenarios.
Critical Zones are agile and easily adaptable spaces that can be broken apart from settings that allow for problem solving activities and private reflective spaces for individuals.
Benefits:
Learning how to think critically assists students in;
- Coming up with innovative solutions to complex problems
- Using deductive reasoning and logic
- Analysing and evaluating possible outcomes
- Being creative and self reflexive
- Fostering independence
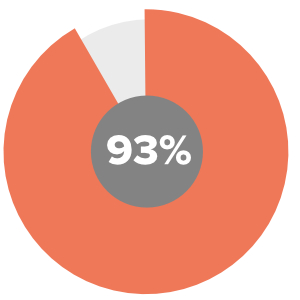
93% of businesses and employers believe “a demonstrated capacity to think critically, communicate clearly, and solve complex problems is more important than an undergraduate major.”
Critical Zone Examples

Create Zones
Create Zones provide the perfect environment for student expression. Featuring colourful and bright spaces with natural lighting to encourage artistic growth. In these spaces, students draw on their curiosity and imagination to pose intriguing questions, explore ideas, environments, and technologies.
Benefits:
Creative thinking teaches students how to;
- Think ‘outside the box’
- How to express themselves
- Remain curious and open to the world
- Experiment with different approaches
- Have fun and take pride in their work
- Develop a life-long love for learning
Employment in the creative industries is growing 40% faster than the Australian economy as a whole. With Australia’s creative sector contributing over $90 billion to our economy’s annual turnover, the need for young Australians to further support this industry is invaluable.
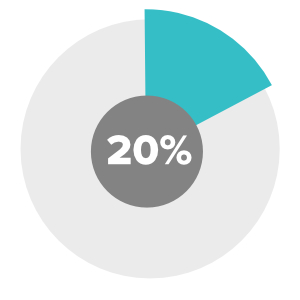
Many of the biggest and most successful businesses in the world allow employees to devote 20% of their work time to thinking creatively and exploring new ideas.
– Source
Create Zone Examples

Culture Zones
Understanding contemporary Australian culture helps teachers build a culturally inclusive learning experience for their students. This starts with broadening cultural and ethnic horizons in a nurturing environment where students feel comfortable in sharing their opinions, ideas and beliefs.
Not only that, when we talk about creating a classroom culture build on kindness, we refer to a universal set of beliefs and actions that guide how students treat one another.
It is important for Future Focused Learners to understand;
- Culture is complex and dynamic
- Culture influences perspectives and identities
- Culture can be expressed in a variety of ways
- Culture can include ways of behaving, thinking, valuing and being
This is especially important because as of 2016, 33.1% of students in NSW a have cultural and language background other than English.
Benefits:
Creating an inclusive classroom culture is crucial for student’s cognitive and emotional development.
Culture Zones incorporate a variety of shared spaces that foster a community of learners as well as support fluid spaces for the individual. This includes large scale soft seating settings and breakout spaces, giving students responsibility and choice in where they learn.
"Inclusive classrooms are classrooms in which instructors and students work together to create and sustain an environment in which everyone feels safe, supported and encouraged to express her or his views and concerns."
Shari Saunders & Diana Kardia, University of Michigan
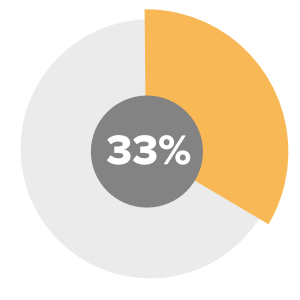
33.1% of students in NSW as of 2016 are of a language background other than English
Culture Zone Examples